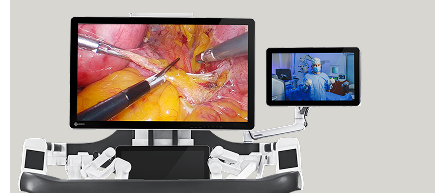
3D-HD Vision
A magnified 3D-HD view aids the surgeon in accurately dissecting and identifying tissues, nerves, and blood vessels.
A magnified 3D-HD view aids the surgeon in accurately dissecting and identifying tissues, nerves, and blood vessels.
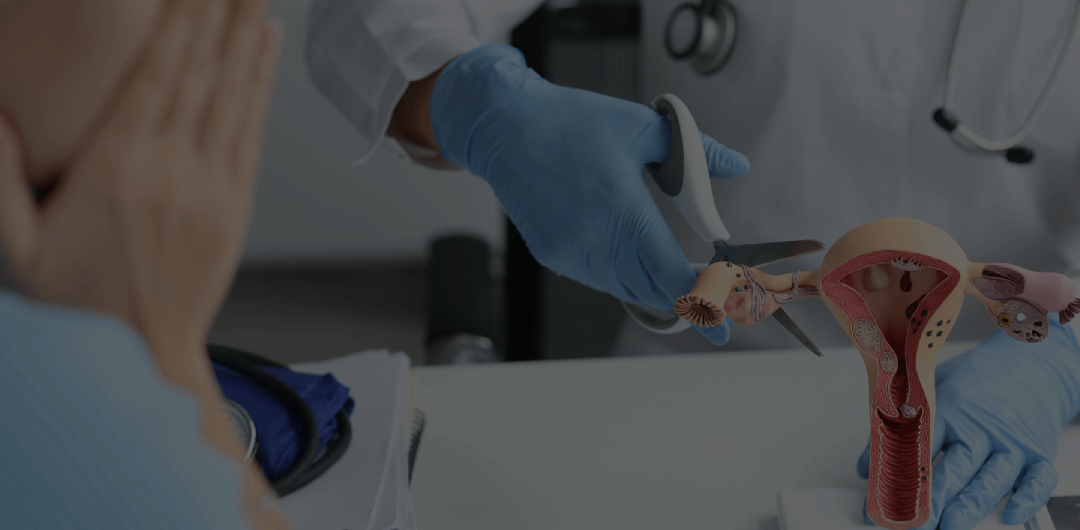



A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that completely or partially removes a person’s uterus.
There are several conditions that may prompt your doctor to recommend a hysterectomy. They range from benign (noncancerous) conditions, like endometriosis or fibroids, to cancer conditions, like endometrial or uterine cancer.
There are several types of hysterectomies that your surgeon will discuss and recommend:
In a partial (supracervical) hysterectomy, the surgeon removes the uterus.
In a total hysterectomy, the surgeon removes the uterus and the cervix.
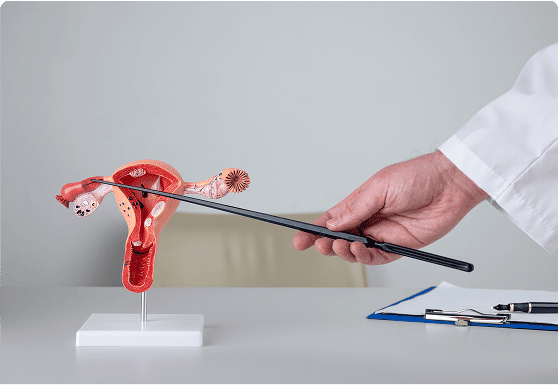
In this surgery, the surgeon removes the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
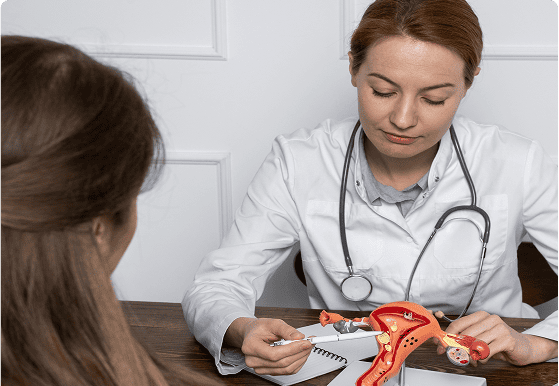
Removes the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries (bilaterally), cervix, supportive ligaments, proximal vagina, and pelvic lymph nodes.
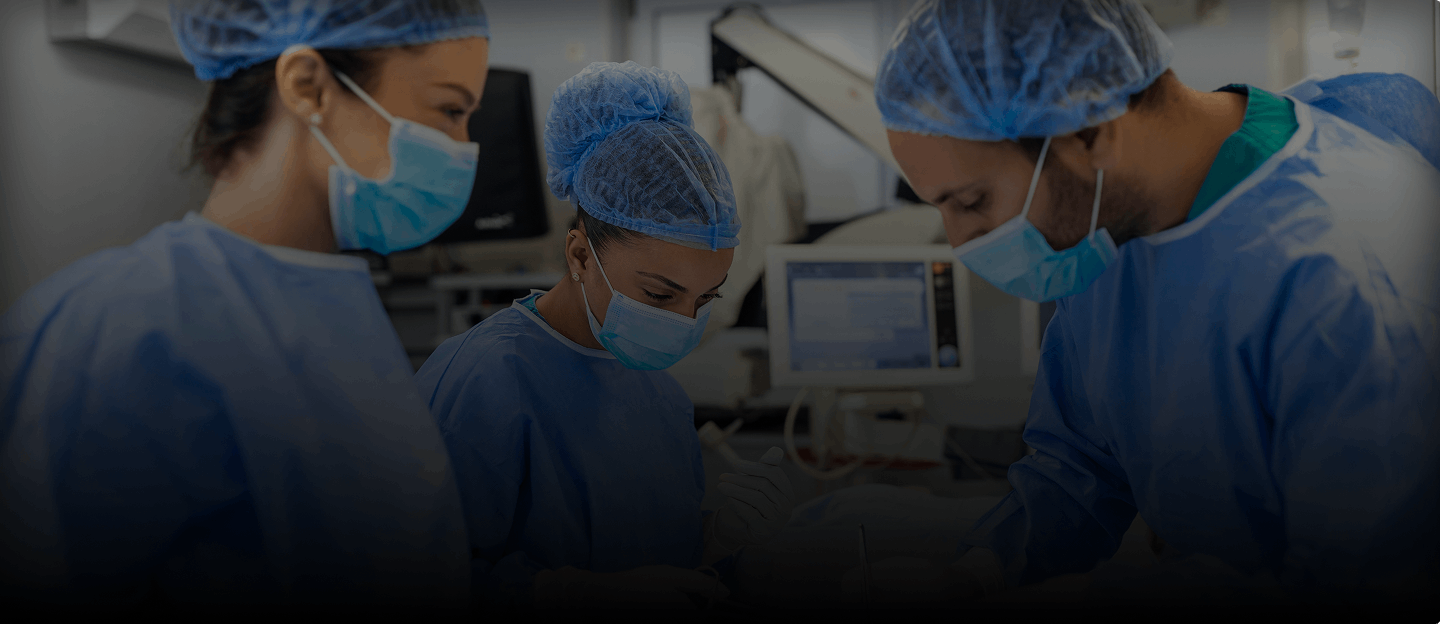

Robotic hysterectomy is a form of advanced laparoscopic surgery wherein it uses a combination of high definition 3D magnification, robotic technology, and miniature wristed instruments to improve the surgeon's ability to view, manipulate, and remove the uterus. The surgeons make 4-5 small incisions for gaining access to robotic arms and instruments. Post-surgery, most women stay 0-1 night in the hospital and 3-4 weeks of reduced activities.
Robotic hysterectomy is a form of advanced laparoscopic surgery wherein it uses a combination of high definition 3D magnification, robotic technology, and miniature wristed instruments to improve the surgeon's ability to view, manipulate, and remove the uterus.
While still in pre-clinical stage, the Mizzo Endo 4000 brings together several high-performance features tailored for next generation care.

A magnified 3D-HD view aids the surgeon in accurately dissecting and identifying tissues, nerves, and blood vessels.
A magnified 3D-HD view aids the surgeon in accurately dissecting and identifying tissues, nerves, and blood vessels.
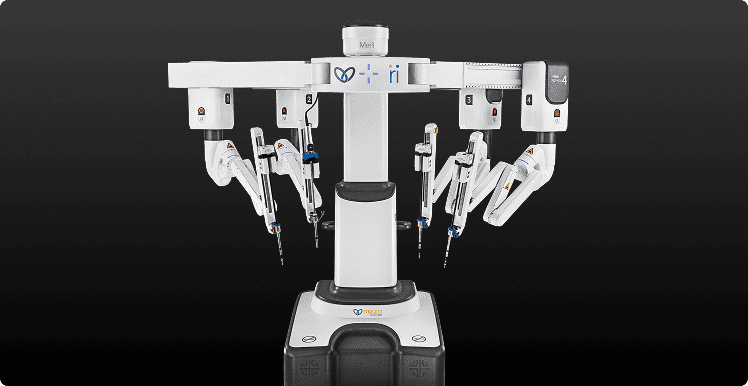
Its slim robotic arms and articulated instruments are ideal for maneuvering in the tight anatomical structures.
Its slim robotic arms and articulated instruments are ideal for maneuvering in the tight anatomical structures.
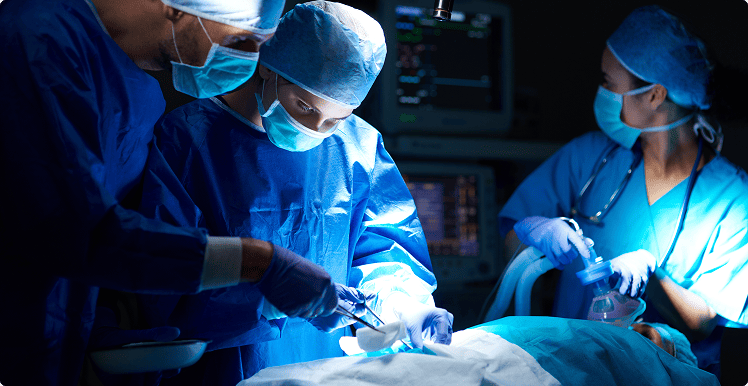
The platform is built to integrate data and live feedback into the workflow, helping surgical teams make better, more informed decisions on the table.
The platform integrates data and live feedback into the surgical workflow, helping teams make better decisions during an operation.
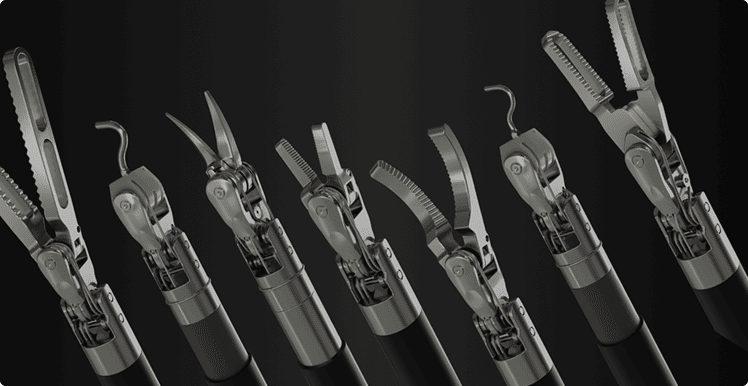
Robotic arms provide the steady, tremor-free movements essential for nerve-sparing surgery.
Robotic arms provide the steady, tremor-free movements essential for nerve-sparing surgery.
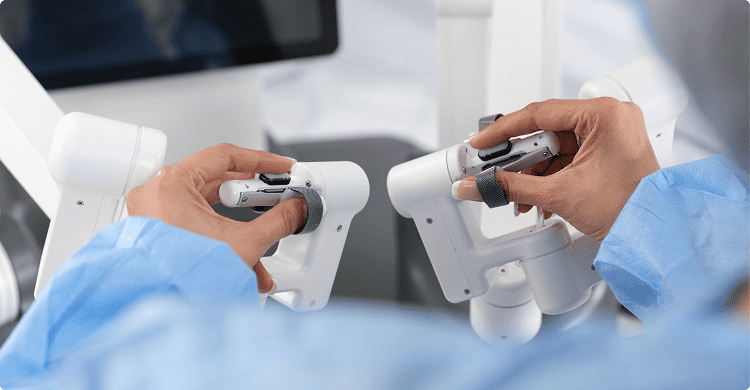
The console reduces the surgeon fatigue and also improves efficiency through customizable controls and immersive visualization.
The console reduces the surgeon fatigue and also improves efficiency through customizable controls and immersive visualization.
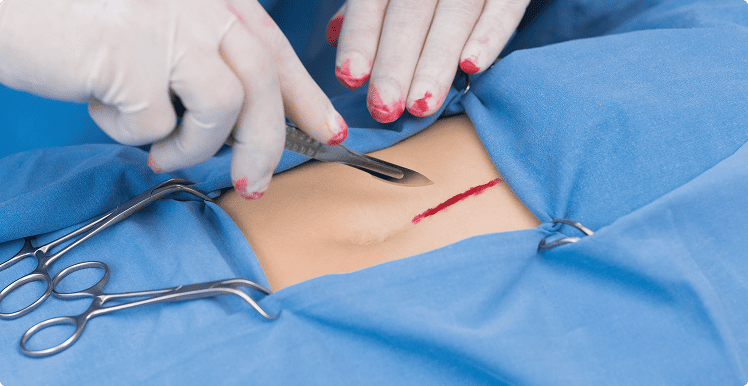
Small incisions mean less pain, smaller scars, and faster healing.
Small incisions mean less pain, smaller scars, and faster healing.
Please reach out to your healthcare provider for any further questions.
Choose the section that best fits your needs
Whether you are a customer with questions or a distributor interested in partnership opportunities, we're here to help.
Choose the section that best fits your needs
Whether you are a customer with questions or a distributor interested in partnership opportunities, we're here to help.
Shekhar, C., Paswan, B. & Singh, A. Prevalence, sociodemographic determinants and self-reported reasons for hysterectomy in India. Reprod Health 16, 118 (2019)